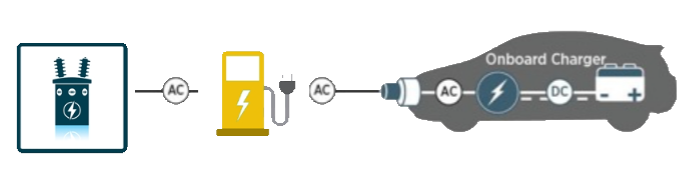
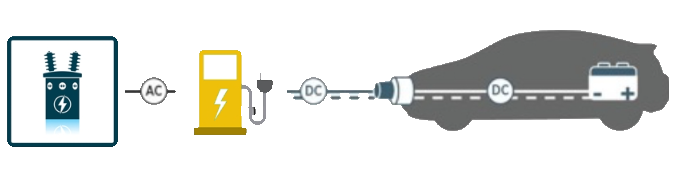
EV Charging
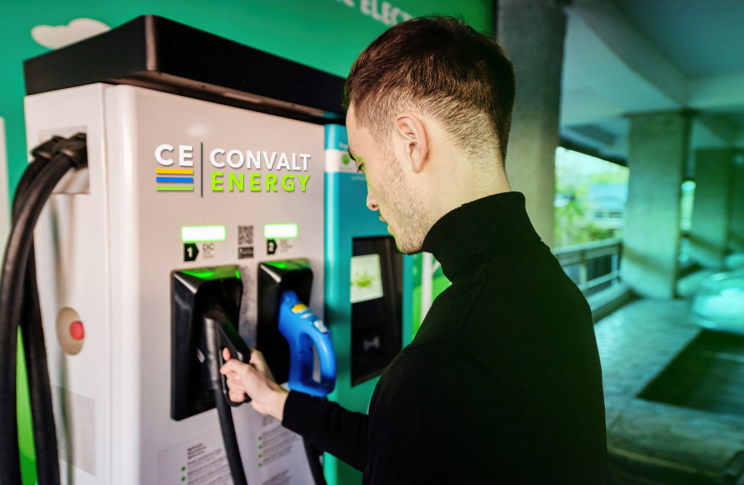

A nationwide expansion strategy is currently under development
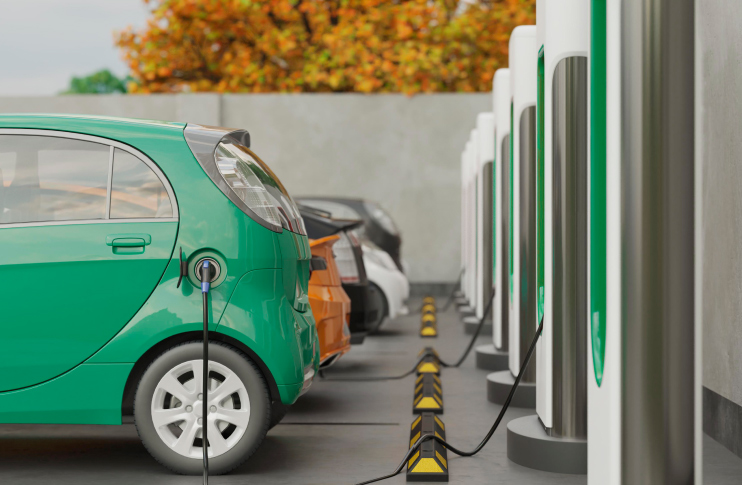
Convalt Energy is currently setting up EV charging stations in New York and other domestic markets, expecting to go live in 2025. Our plan is to set up level 2 and level 3 charging stations. We expect to announce this strategy over the next few months!